Liver diseases are a serious medical concern as the liver performs many vital functions, including detoxifying the body, protein synthesis, and regulating metabolism. Conditions such as hepatitis, fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and others require a comprehensive treatment approach. Here, we’ll explore key methods and recommendations for treating liver diseases to help support the health of this essential organ.
1. Diet for Liver Health
Proper nutrition is crucial in treating liver diseases. It’s recommended to avoid fatty, fried, spicy, and smoked foods that burden the liver. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and adequate water intake. Food should be light and rich in vitamins and antioxidants, which support liver tissue recovery.
2. Medication Therapy

Medication therapy is tailored to the type of liver disease. A doctor may prescribe:
- Hepatoprotectors – drugs that protect liver cells and promote their recovery.
- Antiviral agents – for viral hepatitis to suppress viral activity.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs – to reduce liver inflammation.
It’s essential to follow the doctor’s prescriptions and avoid self-medication, as uncontrolled drug use can worsen liver conditions.
3. Reducing Alcohol and Avoiding Smoking
Alcohol is a major cause of liver damage. People with liver disease should completely avoid alcohol, as it has a toxic effect on liver cells and can worsen their condition. Quitting smoking is also important since the toxins in cigarettes negatively impact the liver.
4. Physical Activity

Moderate physical activity helps improve blood circulation and supports metabolism, which benefits liver health. Light exercises, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, support overall health and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
5. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight increases the risk of fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) and other liver conditions. Weight loss, if necessary, helps reduce liver strain and inflammation. This can be achieved through a combination of healthy eating and physical activity.
6. Vaccination
To prevent viral liver diseases such as hepatitis A and B, vaccination is recommended. Vaccines protect against viral infections that can severely damage the liver and lead to chronic conditions. It’s important to consult a doctor and get the necessary vaccinations if needed.
7. Regular Medical Check-ups
Patients with liver diseases should undergo regular check-ups to monitor liver health and prevent complications. Blood tests, ultrasound, and other diagnostic methods help doctors evaluate treatment effectiveness and adjust therapy as needed.
Liver Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
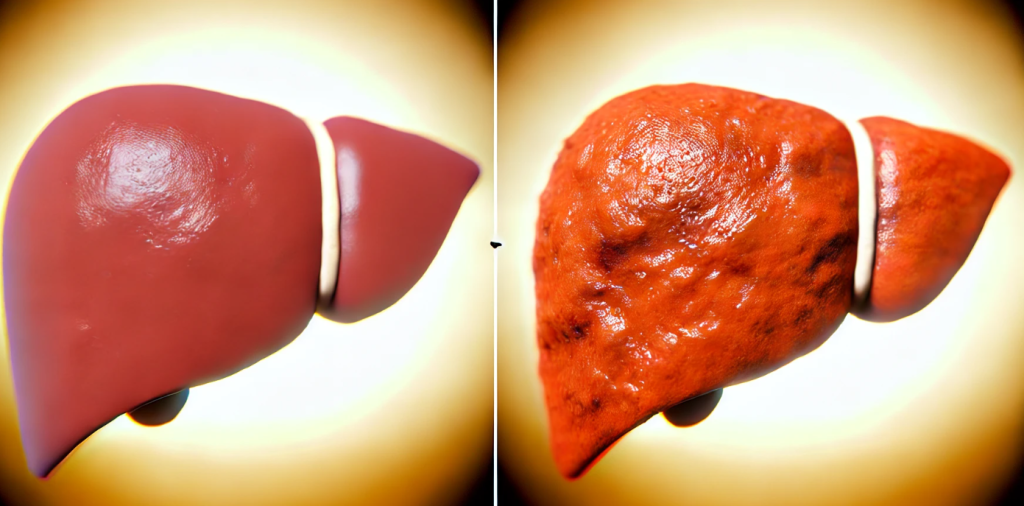
The liver, one of the most vital organs in the human body, plays a central role in metabolism, detoxification, and nutrient storage. However, this multifunctional organ is susceptible to a wide range of diseases that can impair its function and lead to significant health complications. Liver diseases are diverse, ranging from mild, self-limiting conditions to severe, life-threatening disorders. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining liver health and addressing diseases effectively.
Liver diseases can result from various factors, including infections, lifestyle choices, genetic predispositions, and autoimmune conditions. Viral hepatitis, caused by hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E viruses, is a common infectious cause, with hepatitis B and C often leading to chronic liver disease and complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Lifestyle-related liver conditions, such as alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), are increasing in prevalence, driven by excessive alcohol consumption, poor dietary habits, and sedentary lifestyles. Genetic disorders like hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease disrupt the liver’s ability to process iron and copper, respectively, causing damage over time. Autoimmune liver diseases, such as autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells. Additionally, toxins, certain medications, and metabolic syndromes can contribute to liver dysfunction.
Symptoms of liver diseases vary depending on the underlying cause and severity but often include nonspecific early signs. Common symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and abdominal discomfort, typically in the upper right quadrant. As the disease progresses, more specific symptoms may emerge, such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, and itchy skin. Swelling in the abdomen or legs, caused by fluid retention (ascites or edema), is often seen in advanced liver disease. Cognitive changes, including confusion and difficulty concentrating, may occur in cases of hepatic encephalopathy, a condition caused by the accumulation of toxins in the blood due to impaired liver function. Advanced liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, can lead to life-threatening complications, including bleeding disorders, infections, and multi-organ failure.
Diagnosing liver diseases requires a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A detailed medical history and physical examination provide critical insights into potential risk factors and symptoms. Blood tests, such as liver function tests (LFTs), measure levels of enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins to assess liver health. Elevated liver enzymes, like alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), indicate liver inflammation or damage. Additional tests, including viral hepatitis panels, autoimmune markers, and metabolic assessments, help identify specific conditions. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI provide detailed views of liver structure, enabling the detection of abnormalities like tumors, scarring, or fat accumulation. In some cases, a liver biopsy is necessary to confirm a diagnosis and evaluate the extent of liver damage.
Treatment for liver diseases depends on the underlying cause and the stage of the disease. Lifestyle modifications are often the cornerstone of treatment, particularly for conditions like NAFLD and ALD. Reducing alcohol consumption, adopting a balanced diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits and vegetables, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly improve liver health. In cases of viral hepatitis, antiviral medications can suppress the virus and prevent disease progression. Hepatitis C, for instance, is now curable in most cases with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy. Autoimmune liver diseases are managed with immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids and azathioprine, to reduce immune system activity.
Advanced liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or liver cancer, may require more aggressive treatments. Medications to manage complications like ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and variceal bleeding are often used. In cases of liver failure or severe, irreversible damage, liver transplantation may be the only viable option. This procedure replaces the damaged liver with a healthy donor organ, offering patients a chance at long-term survival. Advances in surgical techniques and immunosuppressive therapies have significantly improved transplantation outcomes.
Preventing liver diseases is achievable through proactive measures. Vaccination against hepatitis A and B provides effective protection against these viral infections. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a nutrient-rich diet are critical lifestyle choices for liver health. Practicing safe behaviors, such as using sterile needles and practicing safe sex, reduces the risk of hepatitis transmission. Regular medical check-ups and blood tests can help detect liver issues early, allowing for timely intervention and better outcomes.
In conclusion, liver diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that can have serious health implications if left untreated. Early recognition of symptoms, accurate diagnosis, and a tailored treatment approach are essential for effective management. Advances in medical research, including antiviral therapies and transplantation techniques, have significantly improved outcomes for patients with liver diseases. By adopting a proactive approach to liver health and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce the burden of liver diseases and enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Treating liver diseases involves diet, medication therapy, alcohol avoidance, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, vaccination, and regular medical check-ups. A comprehensive approach helps preserve liver health, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. It’s important to seek timely medical assistance and follow the doctor’s recommendations to maintain liver function.
















Pingback: Sugar Is Killing You: The Alarming Truth Backed by Science (And How to Break Free) - Medhouse.info