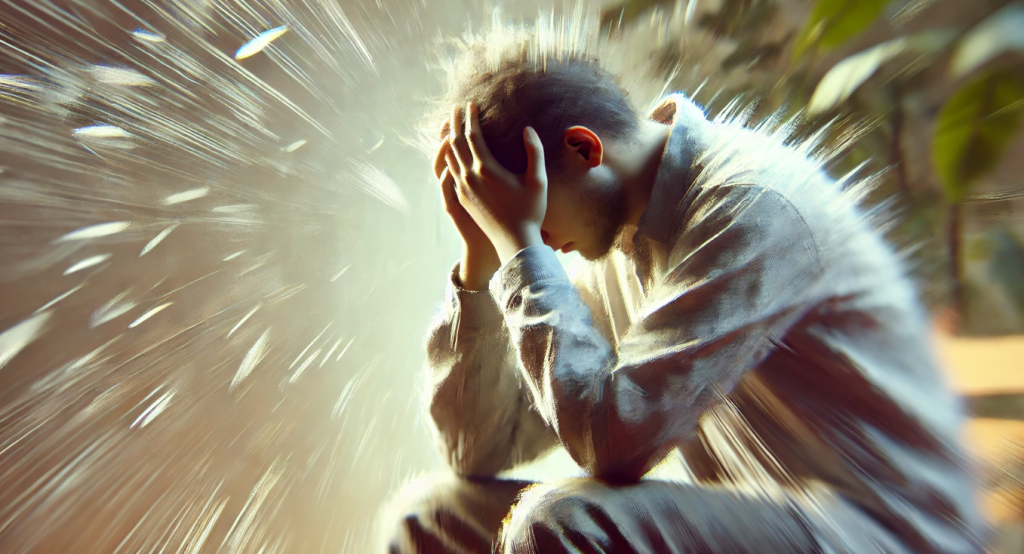
Chronic stress is a prolonged state of emotional and physical tension that can negatively affect health. It increases the risk of developing cardiovascular, immune, and mental health issues. However, there are effective ways to manage chronic stress and improve quality of life.
1. Regular Physical Activity

Physical exercise is one of the most effective ways to cope with stress. Regular activities like yoga, running, or swimming boost endorphin production, improving mood and reducing anxiety.
2. Practicing Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques, such as meditation, breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation, help calm the mind and relax the body. These practices are especially effective with daily use.
3. Creating a Healthy Daily Routine
A daily routine plays a key role in managing stress. Regular sleep, balanced nutrition, and setting aside time for rest help the body handle pressure.
4. Time and Priority Management

Time management helps allocate time effectively, avoiding overload. Learn to say “no” to unnecessary commitments and focus on truly important tasks.
5. Establishing Boundaries in Relationships
Avoid toxic relationships and learn to set personal boundaries. A healthy environment reduces stress levels and improves emotional well-being.
6. Seeking Professional Help
If chronic stress impacts your quality of life, consult a specialist. Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy, helps identify stressors and find ways to manage them.
7. Regular Leisure and Hobbies

Set aside time for hobbies and favorite activities to shift focus and recharge. Activities like drawing, reading, gardening, or walking outdoors can be refreshing.
8. Reducing Screen Time
Excessive screen time can increase feelings of anxiety and fatigue. Limit gadget use before bed to improve sleep quality.
9. Healthy Nutrition
Balanced nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals, supports the body in fighting stress. Avoid excessive caffeine and sugar consumption, which can heighten tension.
10. Support from Loved Ones
Conversations with friends and family help reduce anxiety and better cope with challenges. Social support is a vital element in combating stress.
Managing chronic stress requires a comprehensive approach. Regular care for physical and mental health helps manage pressure and improve overall well-being.
Chronic Stress: Causes, Symptoms, Effects, and Management
Chronic stress is a prolonged and constant state of stress that can negatively impact both mental and physical health. Unlike acute stress, which is short-term and often resolves once the stressor is removed, chronic stress persists over an extended period, often due to ongoing challenges in life or work. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, contributing to serious health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, mental health disorders, and weakened immunity. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies is essential to mitigate the effects of chronic stress and improve overall well-being.
What Causes Chronic Stress?
Chronic stress often results from prolonged exposure to stressors that are not effectively addressed or resolved. Common causes include:
- Work-Related Stress:
- High workloads, tight deadlines, job insecurity, or lack of work-life balance can lead to persistent stress.
- Financial Issues:
- Long-term financial struggles, debt, or economic instability are significant contributors to chronic stress.
- Relationship Problems:
- Ongoing conflicts with family, partners, or friends can create emotional strain.
- Health Issues:
- Managing chronic illnesses or caring for someone with a serious condition can be a constant source of stress.
- Major Life Changes:
- Events such as divorce, relocation, or loss of a loved one may result in sustained stress.
- Social and Environmental Factors:
- Living in unsafe neighborhoods, exposure to discrimination, or social isolation can exacerbate stress levels.
Symptoms of Chronic Stress
Chronic stress manifests in physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. These can vary among individuals but often include:
- Physical Symptoms:
- Persistent headaches, muscle tension, or fatigue.
- Digestive issues, such as upset stomach, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or excessive sleeping.
- Increased susceptibility to colds, infections, or illnesses.
- Emotional Symptoms:
- Irritability, anxiety, or feelings of hopelessness.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Loss of motivation or interest in activities.
- Behavioral Symptoms:
- Overeating or loss of appetite.
- Increased use of alcohol, drugs, or cigarettes.
- Social withdrawal or avoidance of responsibilities.
Over time, these symptoms can lead to severe health complications if left unmanaged.
Effects of Chronic Stress on Health
Chronic stress affects nearly every system in the body and can lead to serious health problems:
- Cardiovascular Health:
- Increases blood pressure and heart rate, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Mental Health:
- Can contribute to anxiety, depression, or burnout.
- May impair cognitive functions such as memory and decision-making.
- Immune System:
- Weakens the body’s ability to fight infections, making individuals more prone to illnesses.
- Digestive System:
- Can exacerbate conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or ulcers.
- Endocrine System:
- Sustained stress raises cortisol levels, which can lead to hormonal imbalances, weight gain, and diabetes.
- Musculoskeletal System:
- Prolonged tension can cause chronic pain or musculoskeletal disorders.
Diagnosing Chronic Stress
While there is no specific test for chronic stress, healthcare professionals assess it through:
- Medical History and Symptoms:
- Discussing physical, emotional, and behavioral signs.
- Psychological Assessments:
- Evaluating stress levels, coping mechanisms, and mental health conditions like anxiety or depression.
- Physical Exams:
- Identifying stress-related health problems, such as high blood pressure or digestive issues.
Managing Chronic Stress
Effective management of chronic stress involves a combination of lifestyle changes, therapeutic interventions, and relaxation techniques. Common strategies include:
- Stress Reduction Techniques:
- Practice mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Engage in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, helps reduce stress hormones and improve mood.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit caffeine, alcohol, and sugar intake, which can exacerbate stress.
- Improving Sleep Hygiene:
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a calming bedtime routine.
- Avoid screens and heavy meals close to bedtime.
- Building a Support System:
- Share concerns with friends, family, or support groups.
- Seek professional counseling or therapy when needed.
- Time Management Skills:
- Set realistic goals, prioritize tasks, and delegate responsibilities when possible.
- Therapeutic Interventions:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help identify and change negative thought patterns.
- Stress management programs or biofeedback techniques can be highly effective.
- Medical Support:
- In severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend medications to manage anxiety or depression linked to chronic stress.
Preventing Chronic Stress
Proactive measures can reduce the likelihood of chronic stress:
- Recognize Early Signs:
- Pay attention to physical or emotional symptoms and address stressors promptly.
- Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms:
- Replace unhealthy habits, such as smoking or overeating, with positive stress-relief methods.
- Set Boundaries:
- Learn to say no to excessive demands and take regular breaks to recharge.
- Foster Resilience:
- Practice gratitude, optimism, and adaptability to better cope with life’s challenges.
- Regular Check-Ups:
- Routine medical and mental health check-ups can help identify and manage stress-related conditions early.
When to Seek Help
Chronic stress requires professional attention if:
- It interferes with daily life, work, or relationships.
- Symptoms persist despite self-care efforts.
- Physical health problems, such as high blood pressure or digestive issues, arise.
Conclusion
Chronic stress is a pervasive issue that can significantly impact both mind and body. Recognizing the causes and symptoms early, combined with adopting effective coping strategies, can help manage stress and improve quality of life. Seeking support from healthcare professionals or therapists is essential for those unable to manage stress independently, ensuring long-term health and well-being.
















Pingback: Unlocking the Secrets of Body Fat Types – Roles, and Tips to Transform Your Health - Medhouse.info