Hormonal imbalance refers to a disruption in the body’s hormone levels, which can lead to significant changes in organ and system function. Hormones regulate numerous processes, from metabolism to emotional well-being. Understanding the key signs of hormonal imbalance can help you seek timely medical advice and prevent complications.
Main Signs of Hormonal Imbalance
1. Weight Changes
Sudden weight gain or loss without obvious reasons may indicate hormonal disturbances.
- Excess cortisol (the stress hormone) can cause fat accumulation in the abdominal area.
- Issues with the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism) may slow down or speed up metabolism.
2. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
In women, irregular periods or their absence may signal imbalances in sex hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This is often associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or pituitary problems.
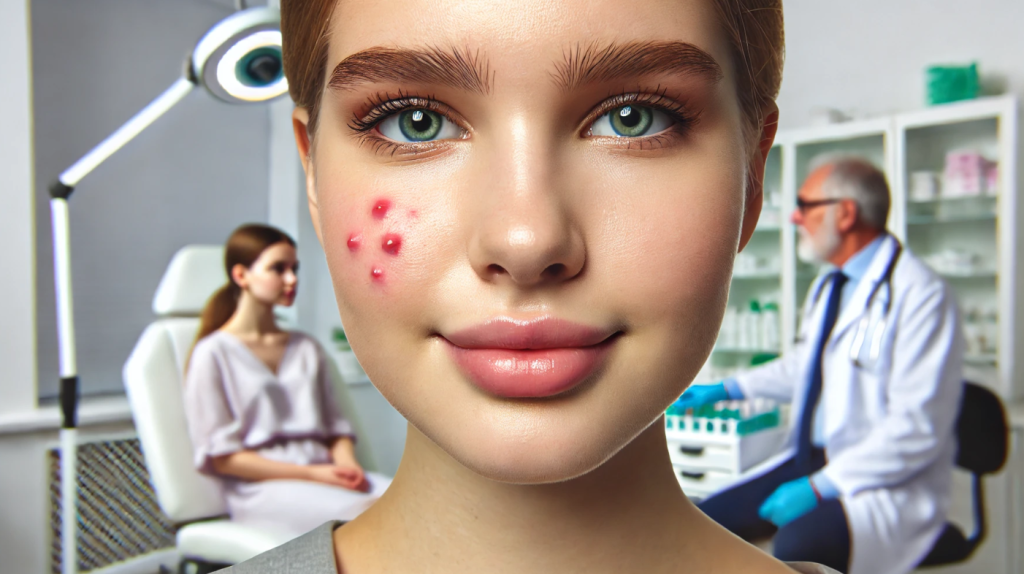
3. Skin Changes
The appearance of acne (especially on the lower face in women) often correlates with elevated testosterone levels. Dry skin may be linked to thyroid dysfunction.
4. Emotional Instability
Excessive irritability, depression, anxiety, or mood swings are often associated with imbalances in cortisol, estrogen, or progesterone.
5. Hair Issues
- Excessive hair loss may be linked to deficiencies in iron, testosterone, or thyroid hormones.
- Increased hair growth on the face and body (hirsutism) is related to elevated androgen levels.
6. Chronic Fatigue
Feeling constantly tired, regardless of sleep, is often connected to adrenal gland issues or thyroid hormone deficiency.
7. Reduced Libido
Low sex drive may result from decreased testosterone levels in both men and women.
8. Sleep Disturbances
Insomnia or excessive sleepiness is often linked to changes in melatonin or cortisol levels.
When to See a Doctor?

Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Multiple symptoms listed above simultaneously.
- Persistent weight, mood, or skin changes.
- Cycle irregularities or chronic fatigue.
Early detection of hormonal imbalances allows effective correction of the problem and prevention of complications.
Hormonal Imbalance: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management
Hormonal imbalance occurs when the body produces too much or too little of certain hormones, disrupting the delicate balance necessary for optimal functioning. Hormones, produced by the endocrine glands, regulate many bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood. When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to various health issues. Hormonal imbalances can affect both men and women, though certain conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), are more common in women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to effectively managing hormonal imbalances.
What Causes Hormonal Imbalance?
The causes of hormonal imbalance vary depending on the specific hormones involved. Common factors include:
- Endocrine Disorders:
- Conditions like hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, PCOS, or diabetes can disrupt hormone levels.
- Age-Related Changes:
- Menopause in women and andropause in men naturally affect hormone production.
- Chronic Stress:
- Prolonged stress triggers the overproduction of cortisol, potentially affecting other hormones.
- Dietary Factors:
- Poor nutrition, excessive sugar intake, or insufficient essential nutrients can lead to hormonal disruptions.
- Medications and Treatments:
- Certain medications, such as steroids or birth control, can alter hormonal balance.
- Underlying Health Conditions:
- Obesity, tumors in endocrine glands, or autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can contribute to imbalances.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Lack of sleep, sedentary habits, and excessive alcohol consumption are known to impact hormone levels.
Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance depend on the hormones affected and may vary between individuals. Common symptoms include:
- General Symptoms:
- Fatigue, weight gain or loss, and mood swings.
- Hair thinning or excessive hair growth (hirsutism).
- Reproductive Symptoms:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles in women.
- Reduced libido or erectile dysfunction in men.
- Metabolic Symptoms:
- Changes in appetite, increased thirst, or frequent urination (linked to insulin imbalances).
- Thyroid-Related Symptoms:
- Hypothyroidism: Cold sensitivity, dry skin, constipation, and sluggishness.
- Hyperthyroidism: Heat intolerance, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
- Adrenal Symptoms:
- Chronic stress symptoms like high blood pressure, sleep disturbances, or weight changes due to cortisol imbalance.
Severe hormonal imbalances can lead to complications such as infertility, osteoporosis, or cardiovascular issues if untreated.
Diagnosing Hormonal Imbalance
Diagnosing hormonal imbalances requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- A review of symptoms, lifestyle factors, and family history of endocrine conditions.
- Blood Tests:
- Measure hormone levels such as estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and insulin.
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI scans may assess the health of endocrine glands, like the thyroid or adrenal glands.
- Specialized Tests:
- Tests like glucose tolerance or pituitary function assessments may be conducted for specific conditions.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Imbalance
Treatment focuses on restoring hormonal balance and addressing the underlying causes. Options include:
- Medications:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Used for menopause, andropause, or conditions like hypothyroidism.
- Birth Control Pills: Regulate menstrual cycles and hormone levels in women with PCOS.
- Insulin or Metformin: Manage blood sugar levels in diabetic patients.
- Anti-Androgens: Reduce testosterone levels in conditions like hirsutism.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
- Include hormone-supportive nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and magnesium.
- Regular Exercise:
- Helps regulate hormones such as insulin, cortisol, and endorphins.
- Stress Management:
- Techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can lower cortisol levels.
- Adequate Sleep:
- Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep to support hormonal regulation.
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Natural and Alternative Remedies:
- Herbal supplements like ashwagandha, maca root, or black cohosh may provide relief for mild imbalances. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Surgery may be required to remove tumors or cysts affecting endocrine glands.
- Specialized Therapies:
- Thyroid hormone therapy for hypothyroidism.
- Radioactive iodine or antithyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism.
Preventing Hormonal Imbalance
Preventing hormonal imbalances involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors. Key steps include:
- Balanced Nutrition:
- Eat a diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins to support endocrine health.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Engage in both aerobic exercises and strength training to improve overall hormonal function.
- Stress Reduction:
- Incorporate stress-relief practices into your routine to avoid cortisol spikes.
- Avoid Endocrine Disruptors:
- Minimize exposure to chemicals found in plastics, cosmetics, and cleaning products that may interfere with hormones.
- Regular Check-Ups:
- Routine health screenings can detect early signs of imbalance for timely intervention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms like severe fatigue, unexplained weight changes, or irregular menstrual cycles. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact physical and emotional well-being, but with proper diagnosis and targeted treatment, they are manageable. By understanding the causes and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain hormonal health. A combination of medical intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive measures ensures a balanced, healthier life.
















Pingback: Causes of Acne: Key Factors Affecting Skin Condition - Medhouse.info
Pingback: Causes of Migraine: Main Factors and Prevention Tips - Medhouse.info
Pingback: You’re Eating Plastic Every Day – Here’s How to Stop It! - Medhouse.info
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?