Joint pain is a common issue caused by injuries, inflammatory diseases, or age-related changes. Timely measures to alleviate pain can improve quality of life and prevent complications. In this article, we’ll explore how to deal with joint pain using evidence-based methods.
Causes of Joint Pain
- Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Inflammation or degenerative changes in the joints are the main causes of chronic pain. - Injuries
Sprains, bruises, or fractures can result in acute pain. - Infections
Certain bacterial and viral infections may affect the joints. - Overuse and Stress
Excessive loads or repetitive movements lead to microtraumas and inflammation.
Methods to Relieve Joint Pain
1. Resting the Joint
Limit strain on the affected joint, especially during the acute phase. This helps reduce inflammation and pain.
2. Using Cold and Warm Compresses

- Cold Compresses reduce swelling and inflammation. They are recommended during the first 48 hours after an injury.
- Warm Compresses improve circulation and relax muscles in cases of chronic pain.
3. Medication
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or diclofenac effectively reduce inflammation.
- Pain-relief creams and gels provide localized relief.
- In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid injections.
4. Physical Therapy
Procedures like ultrasound, laser therapy, or electrophoresis help reduce pain and restore joint function.
5. Regular Physical Exercise
Gentle exercises like yoga or swimming help maintain joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Avoid high-impact activities.
6. Weight Loss
Excess weight increases stress on joints, especially the knees. Reducing body weight helps alleviate pain.
7. Balanced Diet

- Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (fish, nuts, flaxseed oil) to reduce inflammation.
- Add calcium and vitamin D to your diet to strengthen bones.
When to See a Doctor?
- If pain persists for more than 7 days.
- If you notice swelling, redness, or a warm sensation in the joint area.
- If pain limits movement.
Prevention

- Maintain an active lifestyle with moderate exercise.
- Wear comfortable footwear and avoid prolonged standing.
- Perform regular exercises to strengthen joints.
Joint Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment
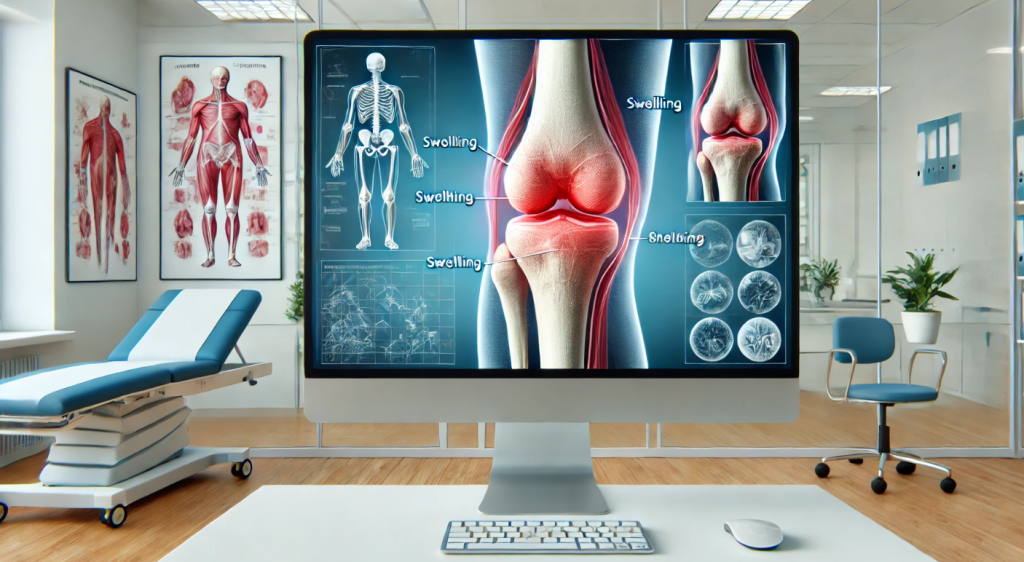
Joint pain is a common health issue that can affect people of all ages, impacting mobility and overall quality of life. It may result from injuries, inflammation, or underlying health conditions. Joints, where two or more bones meet, are critical for movement and flexibility, and pain in these areas can range from mild discomfort to severe, chronic pain. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for joint pain is essential for managing the condition and maintaining an active lifestyle.
Joint pain can occur in any part of the body but is most commonly reported in the knees, hips, shoulders, and hands. The causes of joint pain vary widely, with the most common being arthritis. Osteoarthritis, a degenerative condition, occurs when the cartilage that cushions joints wears away, leading to stiffness, swelling, and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, causes the body’s immune system to attack joint tissues, resulting in inflammation, swelling, and damage. Other conditions that can cause joint pain include gout, a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, and lupus, another autoimmune disease.
Injuries are another frequent cause of joint pain. Sprains, strains, dislocations, or fractures can damage the ligaments, tendons, or bones within the joint, leading to acute pain and limited mobility. Overuse injuries, common in athletes or individuals with physically demanding jobs, can also result in joint discomfort. Infections, such as septic arthritis, or underlying conditions like bursitis and tendinitis, are additional contributors to joint pain.
Symptoms of joint pain depend on the cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include swelling, redness, stiffness, and a decreased range of motion. Pain may be sharp and sudden, as with an injury, or chronic and persistent, as seen in arthritis. In some cases, joint pain may be accompanied by fatigue, fever, or general malaise, indicating a systemic issue.
Diagnosing joint pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. A doctor may ask about the duration and severity of the pain, as well as any activities or conditions that might have triggered it. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasounds are often used to assess joint structure and identify damage or inflammation. Blood tests may also be conducted to detect markers of infection, inflammation, or autoimmune activity.
Treatment for joint pain depends on its cause and severity. For mild cases, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed for conditions involving inflammation, such as arthritis or tendinitis. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain directly in the affected joint.
Physical therapy is often recommended for joint pain, as targeted exercises can strengthen surrounding muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pressure on the joints. Low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, or cycling are particularly beneficial for maintaining joint health without causing additional strain. Assistive devices such as braces, orthotics, or walking aids may also help alleviate pressure and improve mobility.
In cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures like arthroscopy can repair damaged tissue, while joint replacement surgery may be required for advanced osteoarthritis or severe injuries. Advances in medical technology have made joint replacement surgeries more effective, with faster recovery times and improved outcomes.
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing joint pain and preventing further issues. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as excess weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and support overall joint health. Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods, alcohol, or sugar can also positively impact joint function.
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements like turmeric and glucosamine, may complement traditional treatments and provide additional relief for some individuals. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any alternative therapies to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Joint pain can significantly affect daily activities and overall well-being, especially when left untreated. Early intervention is key to managing symptoms and preventing complications. If joint pain persists for more than a few weeks, worsens over time, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms like fever or severe swelling, medical advice should be sought promptly.
In conclusion, joint pain is a common but manageable condition with the right approach. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely treatment are crucial for maintaining joint function and improving quality of life. With a combination of medical care, physical activity, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals experiencing joint pain can regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and lead a more active and fulfilling life.















Pingback: 8 Main Signs of Viral Hepatitis: Symptoms and Diagnosis - Medhouse.info